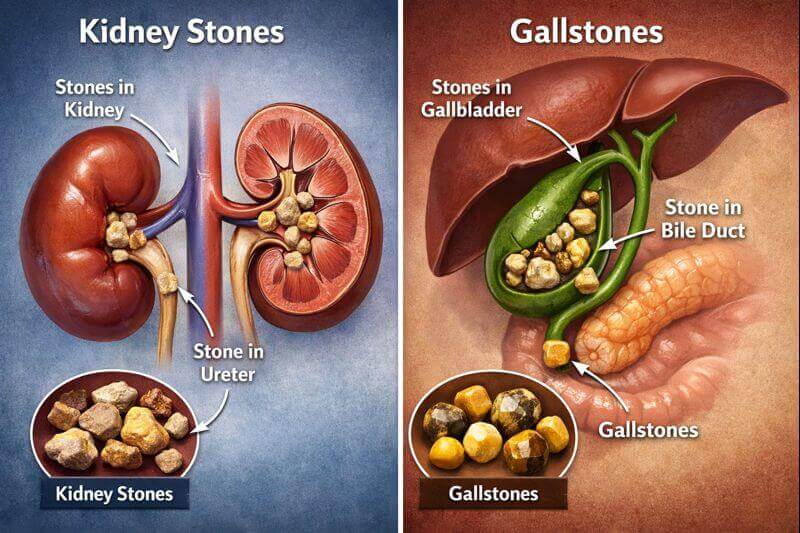
Are Kidney Stones and Gallstones the Same?
Many people believe that kidney stones and gallstones are the same condition, just occurring in different parts of the body. While both involve the formation of hard stones and can cause severe pain, they are entirely different medical problems with distinct causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatments.
Understanding the difference between kidney stones and gallstones is crucial, as early and accurate diagnosis helps prevent serious complications.
What Are Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are hard mineral and salt deposits that form inside the kidneys when urine becomes concentrated. When minerals such as calcium, oxalate, or uric acid build up, they crystallize and form stones.
Kidney stones can remain in the kidney or travel through the urinary tract, often causing intense, wave-like pain.
What Are Gallstones?
Gallstones are solid particles that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver that stores bile. Bile helps in digestion, especially of fats.
Gallstones develop when bile contains too much cholesterol or bilirubin, or when the gallbladder does not empty completely.
Kidney Stones vs Gallstones: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
The table below highlights the key differences between kidney stones and gallstones, making it easier to understand how these conditions differ.
| Factor | Kidney Stones | Gallstones |
| Primary Location | Kidneys and urinary tract | Gallbladder |
| Main Causes | Dehydration, high salt intake, excess calcium or uric acid, family history, metabolic disorders | Excess cholesterol or bilirubin in bile, obesity, rapid weight loss, pregnancy, diabetes |
| Risk Factors | Low water intake, high-protein diet, recurrent UTIs, certain medications | Fatty diet, sedentary lifestyle, age above 40, hormonal changes |
| Common Symptoms | Severe lower back or side pain, pain radiating to groin, burning urination, frequent urination, blood in urine, nausea | Upper right abdominal pain, pain after fatty meals, bloating, indigestion, nausea, vomiting |
| Pain Pattern | Sudden, intense, wave-like pain | Steady or crampy pain, often meal-related |
| Associated Signs | Fever and chills if infection develops | Fever, jaundice, dark urine if bile duct is blocked |
| Diagnosis Methods | Urine tests, blood tests, ultrasound, CT scan | Abdominal ultrasound, blood tests, CT or MRI if required |
| Initial Treatment | Increased fluid intake, pain medications | Observation, pain management |
| Advanced Treatment | Shock wave lithotripsy, ureteroscopy, surgery for large stones | Gallbladder removal surgery (cholecystectomy) |
| Can Stones Pass Naturally? | Yes, if small | No |
| Complications if Untreated | Kidney infection, blockage, kidney damage | Pancreatitis, gallbladder infection, bile duct obstruction |
How Pain Location Helps Identify the Condition
One of the easiest ways doctors differentiate between kidney stones and gallstones is by pain location.
- Kidney stone pain usually starts in the lower back or side and may move toward the groin.
- Gallstone pain is felt in the upper right abdomen and often worsens after eating fatty meals.
Understanding this difference helps patients seek the right specialist sooner.
Can Kidney Stones and Gallstones Occur Together?
Yes, it is possible for a person to develop both conditions, especially if they have:
- Obesity
- Metabolic disorders
- Dehydration
- Poor dietary habits
However, kidney stones and gallstones are not directly related and require different treatment approaches.
Diagnosis: How Doctors Confirm the Condition
Doctors use a combination of symptom history, physical examination, blood tests, and imaging studies to confirm the diagnosis. Ultrasound is commonly used for both conditions, while CT scans provide more detailed information when needed.
Treatment Approaches: Why They Differ
Although both involve stones, treatment strategies differ greatly:
- Kidney stones may pass naturally or require procedures to break or remove them.
- Gallstones often require surgical removal of the gallbladder if symptoms persist.
This is why correct diagnosis is essential.
What Happens If These Stones Are Ignored?
Ignoring symptoms can lead to serious complications.
Untreated Kidney Stones May Cause:
- Recurrent urinary infections
- Kidney damage
- Severe obstruction of urine flow
Untreated Gallstones May Cause:
- Gallbladder infection
- Pancreatitis
- Life-threatening bile duct blockage
Prevention Tips for Both Conditions
Preventing Kidney Stones
- Drink plenty of water
- Reduce salt intake
- Eat a balanced diet
Preventing Gallstones
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Avoid rapid weight loss
- Eat fiber-rich foods
Simple lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of recurrence.
When Should You See a Doctor?
Seek medical care if you experience:
- Severe or persistent abdominal or back pain
- Blood in urine
- Fever with pain
- Pain after meals that doesn’t subside
Early intervention leads to better outcomes.
Final Thoughts: Are Kidney Stones and Gallstones the Same?
Kidney stones and gallstones are not the same, despite similar names. They differ in:
- Location
- Cause
- Symptoms
- Treatment
Recognizing these differences empowers patients to seek timely care and avoid complications.
“Also Read: Gallbladder Pain? Here’s When You Should Visit a Specialist in Dombivli“
➝https://www.samatahospital.com/gallbladder-pain-heres-when-you-should-visit-a-specialist-in-dombivli/
![]()


No Comments
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.