Do Hernias Only Affect Men?
Hernias are commonly believed to be a “man’s problem.” Because men are diagnosed with hernias more frequently, especially groin hernias, many people assume women are not affected. This misconception often leads to delayed diagnosis and treatment in women, increasing the risk of complications.
So, do hernias only affect men? The clear answer is no. Hernias can affect both men and women, although the type, symptoms, and presentation may differ. At Samata Hospital, Dr. Ashish Dhadas, an experienced general and laparoscopic surgeon, treats hernias in both men and women using advanced, minimally invasive techniques.
What Is a Hernia?
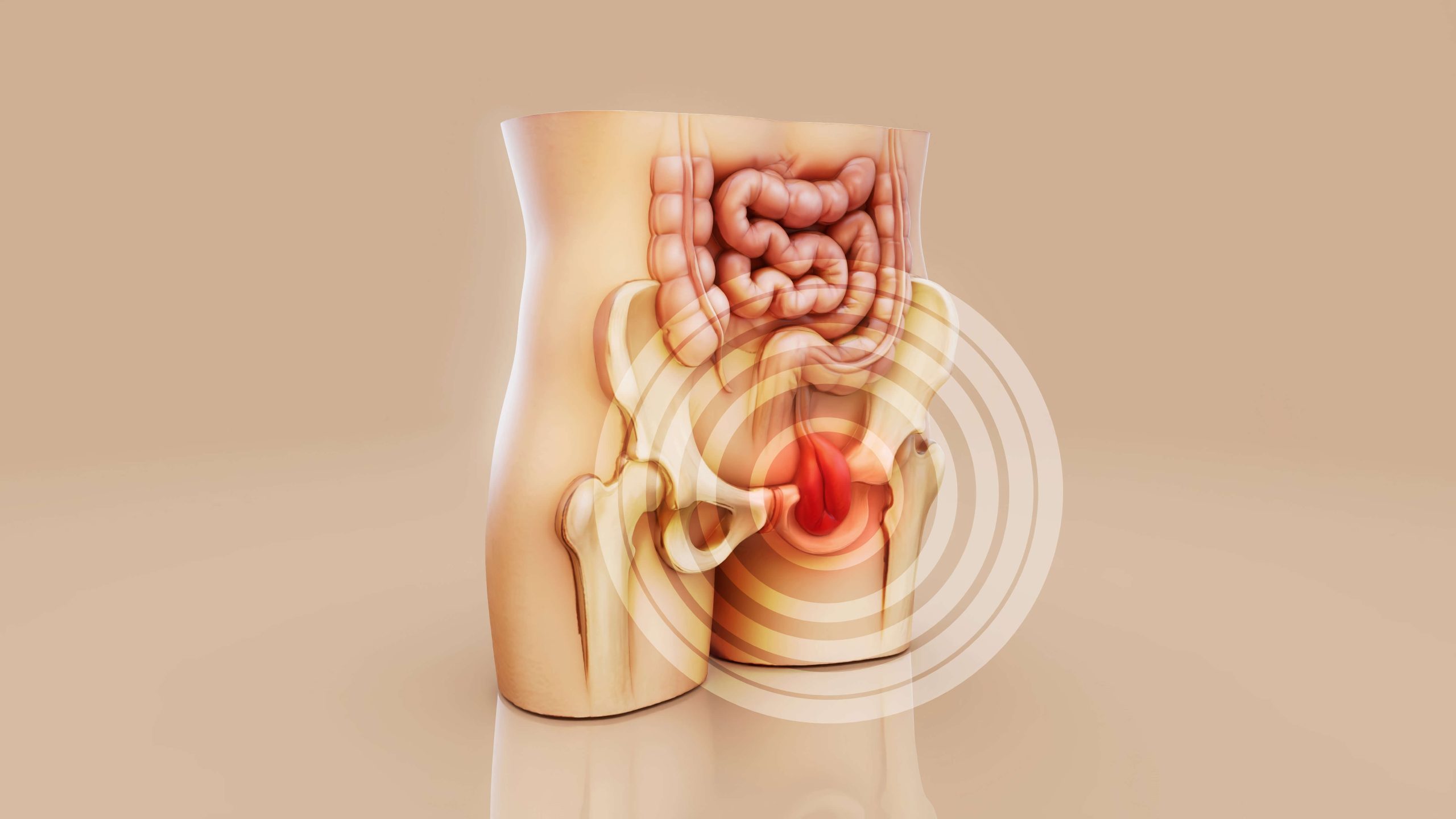
A hernia occurs when an internal organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. This results in a bulge or swelling that may be visible or felt, especially during physical strain.
Hernias most commonly develop in the abdominal wall and groin region but can also occur near surgical scars or the upper abdomen.
Why Are Hernias More Common in Men?
Men are more frequently diagnosed with hernias due to anatomical and lifestyle factors.
Reasons Include:
- A naturally weaker area in the groin due to the passage of the spermatic cord
- Higher likelihood of inguinal hernias
- Greater involvement in heavy physical activity
- Higher prevalence of smoking and chronic cough
Because inguinal hernias are the most common type, and they occur more often in men, hernias are wrongly labelled as a male-only condition.
Can Women Get Hernias?
Yes, women can and do get hernias. However, they often experience:
- Different types of hernias
- Less obvious symptoms
- Higher chances of misdiagnosis
This makes awareness especially important.
Types of Hernias in Women
1. Femoral Hernia
Femoral hernias are more common in women, especially after pregnancy.
Symptoms may include:
- Pain or discomfort in the groin
- A small, hard-to-notice lump
- Pain worsening while standing or lifting
Femoral hernias have a higher risk of complications and often require early surgical treatment.
- Inguinal Hernia in Women
Although more common in men, women can also develop inguinal hernias.
Symptoms include:
- Groin pain
- Discomfort during physical activity
- Mild swelling that may come and go
- Umbilical Hernia
Occurs near the belly button.
Common in:
- Women after pregnancy
- Individuals with obesity
Umbilical hernias may become more noticeable over time.
- Incisional Hernia
Develops at the site of a previous surgical incision.
Risk factors include:
- Multiple abdominal surgeries
- Poor wound healing
- Obesity
- Hiatal Hernia
Occurs when part of the stomach moves into the chest cavity.
Symptoms include:
- Acid reflux
- Chest discomfort
- Difficulty swallowing
This type affects both men and women equally.
Symptoms of Hernia in Women vs Men
Common Symptoms in Men
- Visible groin bulge
- Pain during lifting or coughing
- Heaviness in the groin
Common Symptoms in Women
- Dull pelvic or groin pain
- Discomfort without visible bulge
- Pain mistaken for gynecological issues
Because symptoms in women are often subtle, diagnosis may be delayed.
Why Hernias in Women Are Often Missed
Hernias in women are frequently misdiagnosed due to:
- Smaller bulges
- Deeper location of femoral hernias
- Symptoms overlapping with gynecological or urinary conditions
Delayed diagnosis increases the risk of:
- Strangulation
- Intestinal obstruction
- Emergency surgery
When Should Women Worry About a Hernia?
Women should seek medical evaluation if they experience:
- Persistent groin or lower abdominal pain
- Pain that worsens with standing or exertion
- A lump that becomes painful
- Sudden severe pain with nausea or vomiting
These may indicate a complicated hernia.
Hernia Diagnosis
At Samata Hospital, hernia diagnosis involves:
Clinical Examination
- Physical assessment while standing and coughing
- Evaluation of pain and swelling
Imaging Tests
- Ultrasound
- CT scan or MRI (especially helpful in women with unclear symptoms)
Accurate diagnosis ensures appropriate treatment planning.
Hernia Treatment: Is Surgery Always Needed?
Can Hernias Heal on Their Own?
No. Hernias do not heal without treatment. Over time, they tend to grow and cause symptoms.
Surgery is the only definitive treatment for hernias.
Modern techniques include:
- Laparoscopic hernia surgery
- Mesh repair
- Minimal scarring
- Faster recovery
Early surgical repair prevents complications and improves quality of life.
Why Early Hernia Treatment Is Important
Delaying hernia surgery can lead to:
- Increased pain
- Hernia enlargement
- Intestinal obstruction
- Strangulation (cut-off blood supply)
Women, in particular, are at higher risk of emergency complications with femoral hernias.
Why Choose Samata Hospital for Hernia Treatment?
Samata Hospital offers comprehensive hernia care with modern facilities and experienced surgeons.
Expertise of Dr. Ashish Dhadas
Dr. Ashish Dhadas is a skilled general and laparoscopic surgeon known for:
- Accurate hernia diagnosis in both men and women
- Expertise in minimally invasive hernia repair
- Reduced post-operative pain
- Faster return to daily activities
Each patient receives personalised care based on their hernia type and lifestyle needs.
Preventing Hernias: Is It Possible?
While not all hernias can be prevented, risk can be reduced by:
- Maintaining healthy body weight
- Avoiding heavy lifting
- Treating chronic cough and constipation
- Strengthening core muscles
- Seeking early medical advice for groin pain
Final Thoughts: Hernias Are Not Just a Men’s Problem
Hernias do not affect only men. Women are equally at risk, and in some cases, may face more serious complications due to delayed diagnosis. Awareness, early evaluation, and timely treatment are key to preventing long-term problems.
At Samata Hospital, Dr. Ashish Dhadas provides expert hernia care for both men and women, ensuring safe treatment and optimal recovery.
“Also Read: Gallbladder Pain? Here’s When You Should Visit a Specialist in Dombivli“
➝https://www.samatahospital.com/gallbladder-pain-heres-when-you-should-visit-a-specialist-in-dombivli/
![]()


No Comments
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.